Whitepaper EU-AI-Act

AI at X: Privacy Concerns, GDPR Violations, and Misinformation
The rise and rapid development of AI technologies brings significant benefits, such as enhanced user experience and functionality on platforms such as X, Instagram or Facebook. However, it also raises urgent questions about privacy practices, particularly regarding collecting and using personal data without informed consent.
In addition, with hundreds of millions of users actively using platforms such as X, the potential for misinformation propagated by AI models raises concerns due to its potential impact on the course of human events.
In this article, we'll take a closer look at the current practices of AI model training at X as well as its potential impact on data protection and spreading misinformation.
Table of Contents:
Understanding Grok, X's AI Model
X's AI model, Grok, is a large language model (LLM) designed to process and generate human-like text based on vast datasets. It can interpret user intent and context, resulting in more meaningful interactions, and it continuously learns from ongoing user engagement, enhancing its responses over time. Grok was designed as an AI search assistant for premium account holders on X, developed by Musk's US-based company, xAI Corp.
The training methodology for LLMs like Grok heavily relies on user-generated content sourced particularly from X. Grok is trained on millions of posts, comments, and interactions within the platform. By analyzing this data, Grok identifies trends, sentiments, and language nuances that inform its responses.
As such, user posts play a crucial role in shaping the behavior and performance of AI models such as Grok. They provide the foundational context from which the model learns about various topics and user preferences.
And this reliance on personal content raises significant privacy concerns under GDPR.
Possible GDPR Violations of the AI Training Model
In August 2024, noyb - European Center for Digital Rights, a non-profit organization in support of the GDPR, raised a complaint to nine GDPR regulatory bodies in Ireland, Austria, Belgium, France, Greece, Italy, Netherlands, Spain and Poland stating that X has been unlawfully using the personal data of more than 60 million users in the EU/EEA to train its AI technologies (like "Grok") without their consent.
The complaint outlined the following facts:
In September 2023, X added this sentence to its privacy policy:
"We may use the information we collect and publicly available information to help train our machine learning or artificial intelligence models for the purposes outlined in this policy."
According to noyb, in May 2024 X started training its AI Model with posts of EU-based users without further notifying them or asking for their consent.
Additionally, in July 2024, X added a new setting in the X web user interface allowing one's interactions on the platform to be used for training its AI model. This setting was turned on by default. The data may even be shared with xAI, a separate Elon Musk-led company building artificial intelligence that includes but is not limited to Grok.
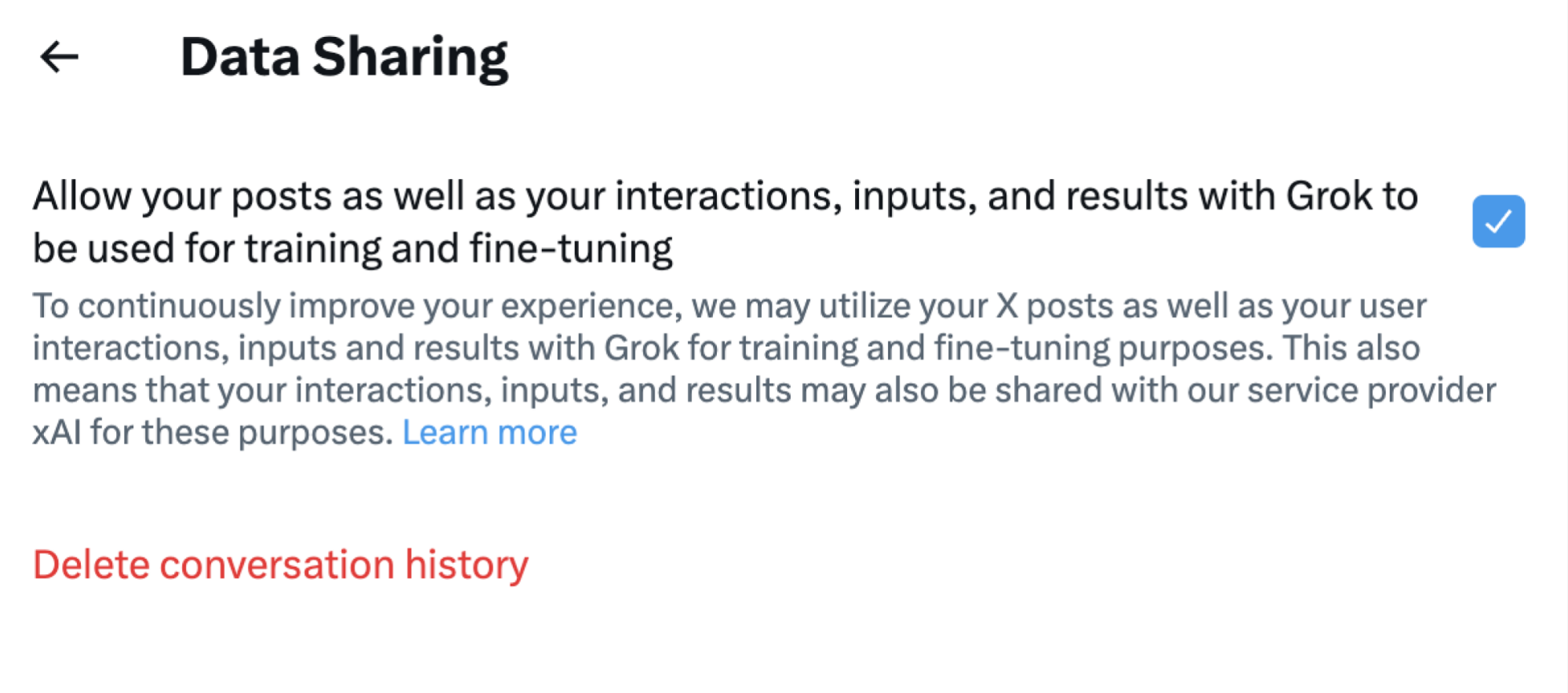
The complaint also explains how opting out of this data sharing violates users' "right to object" under Article 21 of the GDPR, by requiring users to take 7 steps before they are able to turn the setting off, including logging into X, navigating the settings menu, and opening multiple submenus before turning off the data-sharing setting.
Overall, noyb alleges X's actions violate several GDPR provisions including GDPR principles, transparency rules, and operational rules.
Legal Proceedings and Future Implications
In August 2024, the Irish Data Protection Commission (DPC) launched proceedings in Ireland's High Court against Twitter International Unlimited Company, X's main subsidiary in Ireland. The proceedings related to the use of the personal data of X users to train Grok, its AI model.
As a result, X has agreed to suspend the processing of personal data collected between May and August 2024. The proceedings were then terminated in September 2024, after X agreed to permanently discontinue the processing of some of the personal data.
As such, so far, X has managed to avoid any sanctions, although further EU GDPR complaints relating to the training of Grok are still under investigation.
The case has unearthed a potential loophole - once an LLM is trained on personal data, reversing the AI training process is challenging or impossible, making it difficult for data subjects to exercise their right to erasure under the GDPR. This has prompted DPC's request to the European Data Protection Board (EDPB) for a "proactive, effective and consistent Europe-wide regulation," about AI companies using social media posts to train their models.
X's Response and Privacy Concerns
On August 7, 2024 X's Global Governance team tweeted:
"The order that the Irish DPC has sought is unwarranted, overboard and singles out X without any justification. This is deeply troubling...While many companies continue to scrape the web to train AI models with no regards for user privacy, X has done everything it can to give users more control over their data."
The response raises further concerns about data protection and user privacy being at the forefront of the platform's focus, along with concerns about the platform's ability to address issues like hate speech, misinformation, and user safety. In June 2023, X received legal notices from the Australian government demanding explanations about its policies on hate speech. Later that year, X faced pressure to adhere to the European Union's strict Digital Services Act, particularly regarding rules on managing disinformation.
see also: Understanding the EU's Digital Services Act: A Guide for Businesses
Elon Musk's Leadership and Misinformation
The concerns over privacy and misinformation have increased since Elon Musk's $44 billion acquisition of Twitter in 2022. The new management style has led to more aggressive monetization strategies, often prioritising rapid growth over user privacy safeguards, raising concerns about how personal data is handled.
Additionally, Musk himself, the most followed user on X with more than 200 million followers has done little to increase the perception of X as a regulated platform, often contributing to misinformation himself. Though Musk has shared a wide range of misinformation on X, here are some examples:
- In 2020, as the U.S. lockdowns lockdowns to limit the spread of Covid, Musk made a bold prediction on Twitter: “Based on current trends, probably close to zero new cases in US […] by end of April” even claiming children were "essentially immune" to Covid
- In 2023, Musk settled fraud allegations with the Securities and Exchange Commission by agreeing to a $20 million fine for a misleading comment that "led to significant market disruption".
- In 2024, according to the Center for Countering Digital Hate, the X CEO, an avid supporter of Donald Trump in the upcoming US presidential elections, shared 50 misleading or false tweets about the U.S. election amassing over 1.2 billion views in total. This included sharing a deepfake video of Kamala Harris the Democratic candidate, without disclosing that it was manipulated. In the manipulated video, Harris was proclaiming "I am the ultimate diversity hire.”
- In addition to that, in September 2024, X fired the safety team responsible for battling deceptive material on the platform, short ahead of the US presidential elections in November 2024.
- In August 2024, five secretaries of state sent an open letter to Musk urging him to "immediately" make changes to X's AI chatbot, Grok, which had generated false claims about Harris missing a ballot deadline in nine states—misinformation seen by millions of users.
Musk’s public behavior has contributed to ethical concerns and contributed to skepticism among users about X's ability to manage information responsibly and maintain secure practices.

Whitepaper EU-AI-Act
Conclusion
With over 430 million users worldwide, X's influence and reach have become a cause for concern. The platform's role in spreading misinformation, its lack of transparency regarding manipulated content and its lack of regard for data protection and transparency, have raised questions about its commitment to ethical practices.
In conclusion, X faces significant challenges in addressing privacy concerns and misinformation on its platform. The potential GDPR violations in its AI model training process highlight the need for stricter compliance measures to protect user data.
Elon Musk's leadership has brought both innovation and controversy, with his approach to misinformation and privacy issues drawing widespread criticism.
To rebuild trust, X must prioritize transparency, strengthen its data protection policies, and ensure ethical use of AI technologies.
Important: The content of this article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. The information provided here is no substitute for personalized legal advice from a data protection officer or an attorney. We do not guarantee that the information provided is up to date, complete, or accurate. Any actions taken on the basis of the information contained in this article are at your own risk. We recommend that you always consult a data protection officer or an attorney with any legal questions or problems.


