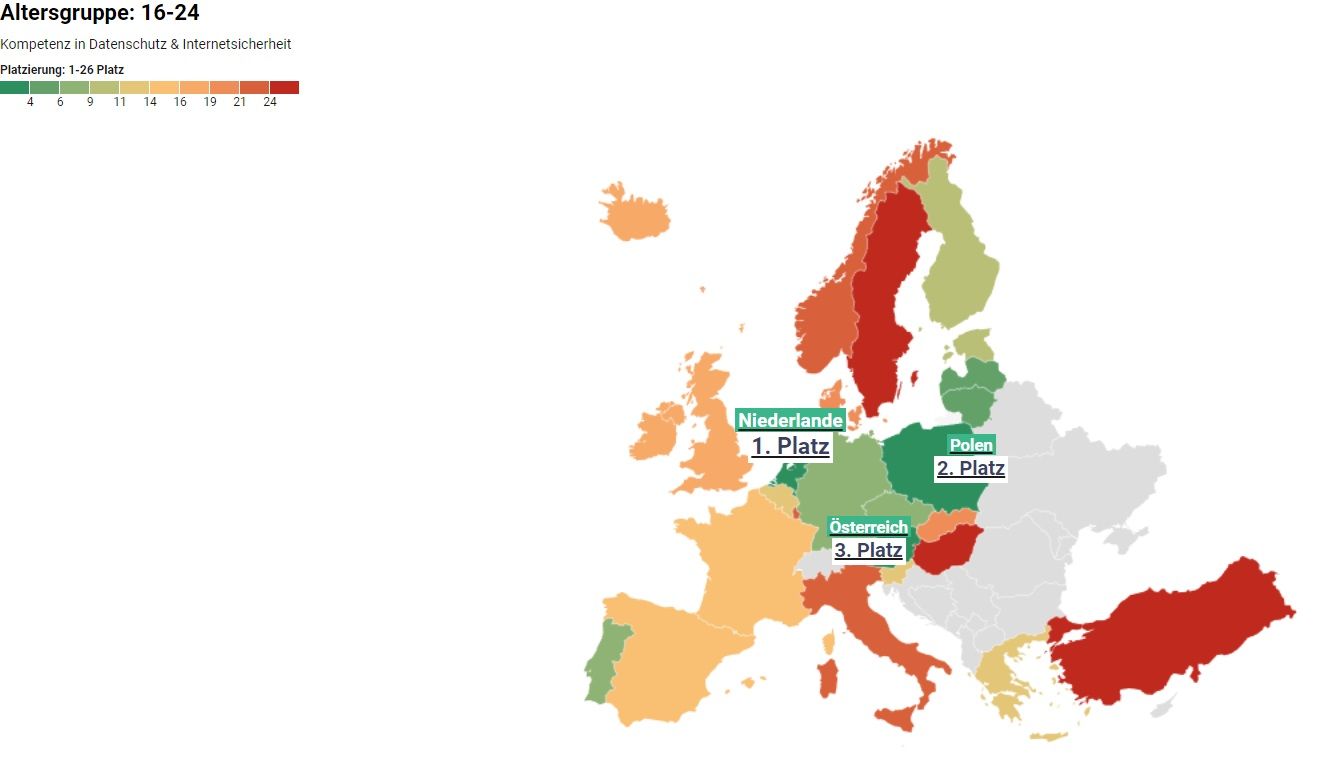
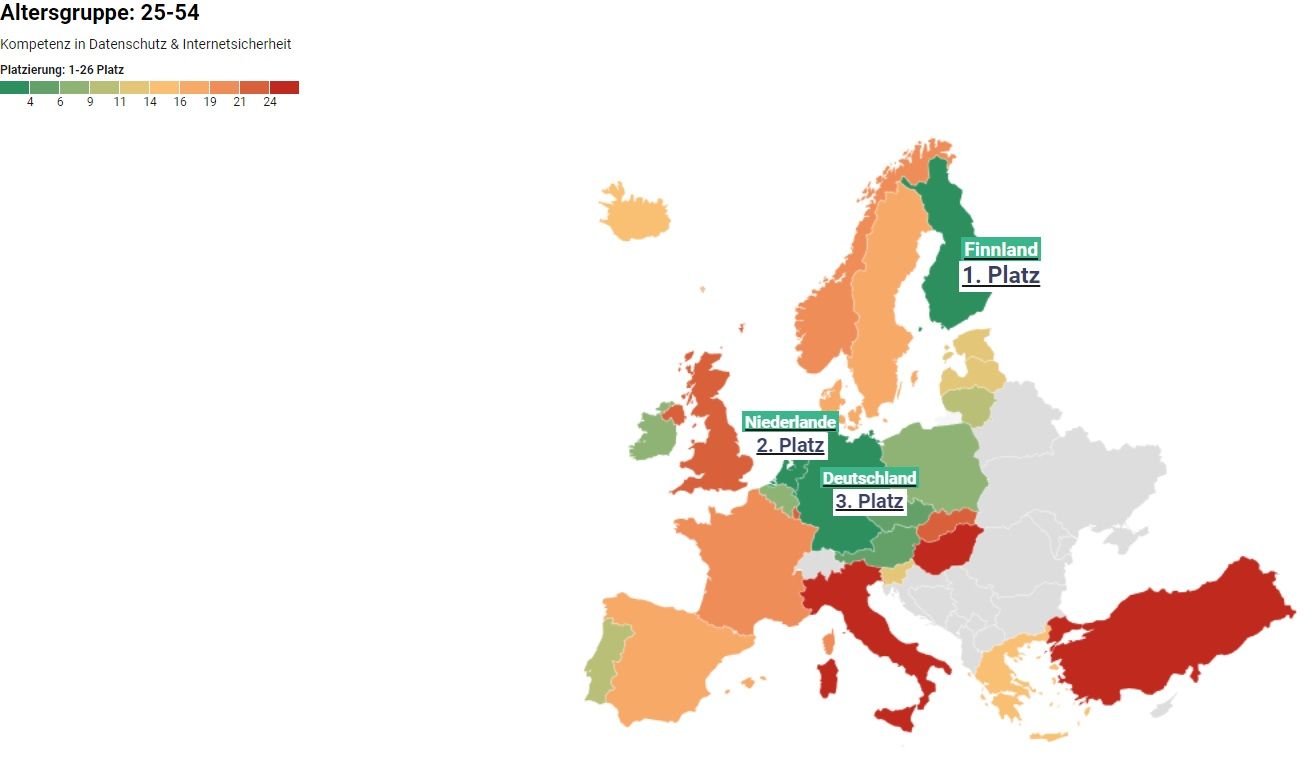
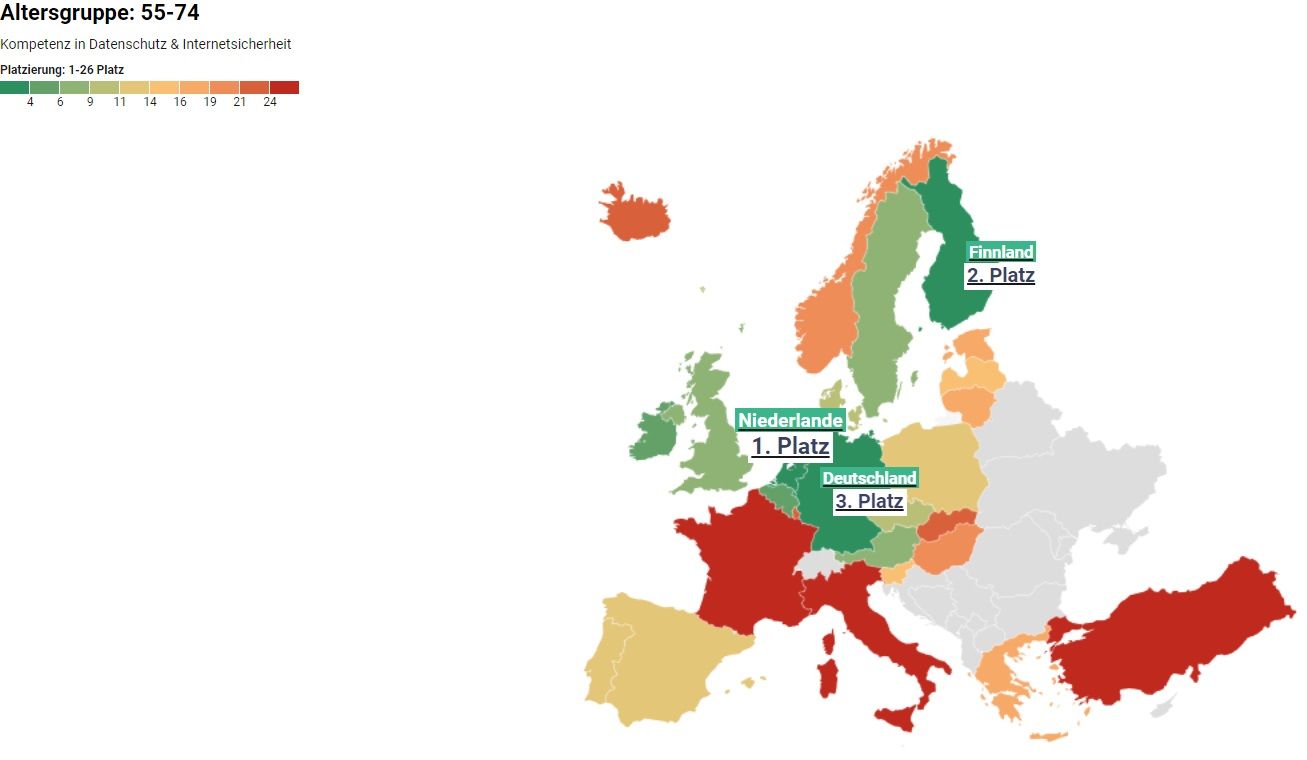
Safe surfers: These are the most security-conscious people in Europe
Due to the steadily increasing digitalization, the GDPR was introduced as an EU regulation in 2018. Standardized data protection is intended to ensure that internet users have full control over how their data is used. Companies and private individuals across Europe had to adapt to these measures and rules in order to make the internet a safer place. How well people in Europe have adapted to the GDPR provides insight into how security-aware and internet-savvy people are in different European countries. heyData conducted a study to find out which European countries are the safest online, highlighting differences between countries and between different age groups. Using data from the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, we examined EU countries as well as Norway, Turkey, Iceland, and the United Kingdom, and analyzed the following age groups: 16–24, 25–54, and 55–74.
The study focuses on the following factors to identify security-conscious and internet-savvy individuals:
People who have not had a virus on their PC in the last three months
People who have not had a virus on theis PC in the last three month
People who use anti-tracking software
The level of privacy settings of individuals on social media
People who protect their personal data from advertisers
Individuals who were not affected by payment fraud
Whether a person prevents or restricts cookies
Based on these factors, we were able to create a ranking that shows where people are safest when using the internet.