
Data protection ranking in Europe
The European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) was enacted in May 2018, and has been internationally recognized as a milestone in data protection history. It standardized rules for protecting personal information across the EU, aiming to achieve a common high level of data protection. In today's digital world, personal data can generate high financial returns, but individuals have limited control over their information. The GDPR created a web of rights and obligations that gives consumers power and control over their data.
As proven experts in data protection, heyData has worked closely with many companies. After three years since the introduction of the GDPR, we conducted a study to evaluate the level of data protection in European countries and identify areas for improvement. Our analysis covered EU member states, Norway (which implemented the EU GDPR), and the United Kingdom (before Brexit).
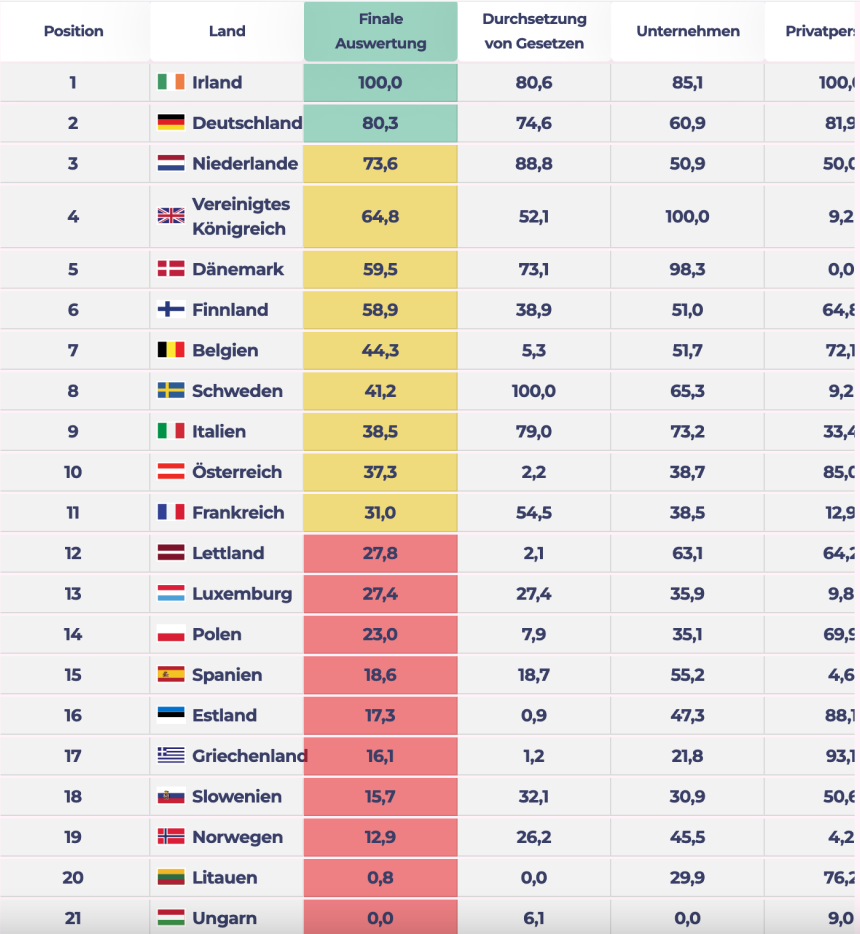
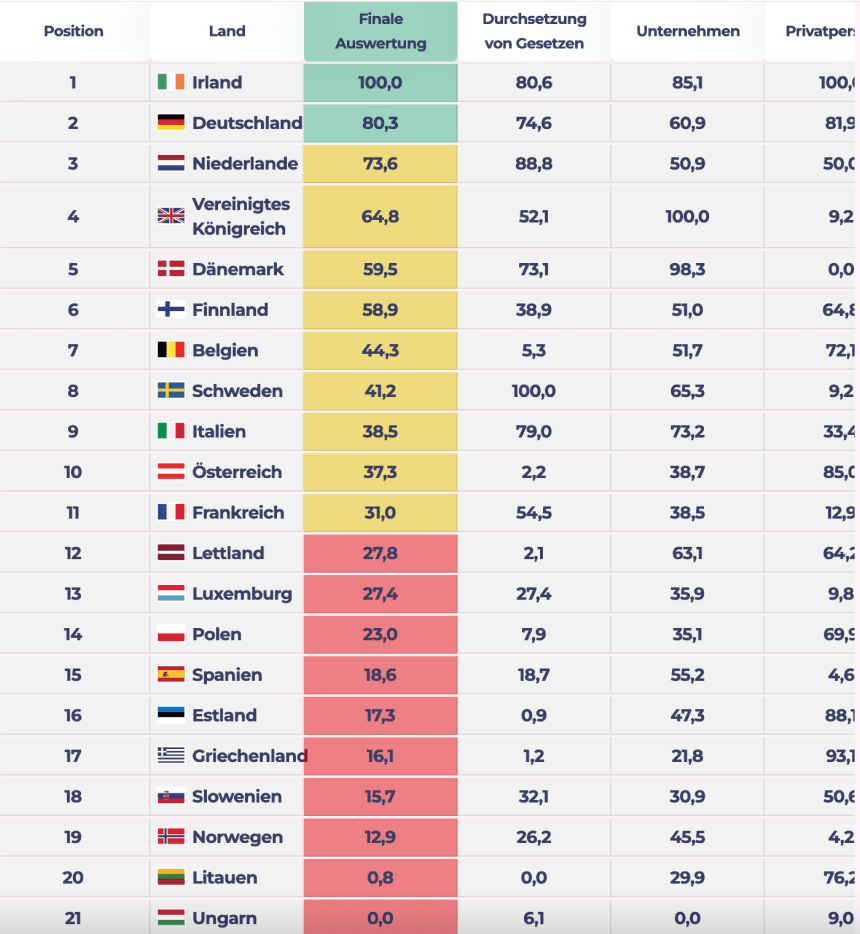
The study focuses on five overarching categories, which we evaluated in 24 subsections using data and statistics from trusted sources, such as the European Commission or the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, among others. A comparison of the EU countries was made possible by implementing a simple mathematical scoring system. The result is the following data protection ranking, which shows the nations with the actual highest level of data protection - Ireland, Germany and the Netherlands - at the top.
The winners of the data protection rankings
 Results
Results
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consetetur sadipscing elitr, sed diam nonumy eirmod tempor invidunt ut labore et dolore magna aliquyam erat, sed diam voluptua. At vero eos et accusam et justo duo dolores et ea rebum. Stet clita kasd gubergren, no sea takimata sanctus est Lorem ipsum dolor.
Enforcement of laws
Data protection breaches, data protection breaches in the pandemic year, fines
Businesses
Data protection strategy, data protection team, voluntary continuing education mandatory, continuing education, data loss, data leakage, insurance coverage

Private individuals
Smartphone malware, computer malware, payment fraud, phishing

Data protection competence
Advertising, browser, cookies, tracking, social media, apps, cloud

Public opinion
Fear of data misuse, authority over data



